This post discusses variation in insecticide chemical structures that share the same MOA, including natural and synthetic products, ordered roughly by weight of pesticide use in California during 2016 (O’Malley M. “Pesticides”, in Current Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 6th Edition. Edited by J. LaDou Robert Hearrison, McGraw-Hill, 2021).
Individual MOAs fall into the following groups:
Multi-site activity compounds, IRC -8 – Halogentated Fumigants, MITC releasers, elemental sulfur, Arsenic compounds
Disruptors of nervous system function
Cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitors, affecting Central Nervous System (CNS) and autonomic nervous system
nicotine and synthetic modulators of nicotinic receptors
Sodium channel modulators and blockers
GABA-gated chloride channel antagonists,
Ryanodine receptor modulators, IRC 28
Octopamine receptor agonists, IRC 19
Chordotonal TRPV channel modulators
DISRUPTORS OF ENERGY METABOLISM
Electron transport chain disruptors; ATP-synthase, uncouplers of oxidative-phosphorylations
MOA’s interfering with insect development
Inhibitors of lipid,, chitin synthesis
Ecdysone receptor agonists, IRC 18 , triazine moulting disruptors, IRC 17, Juvenile hormone mimics IRC 7
Pheromone compounds – interfering with population at highairbone concentrations, used as lure together with insecticides (pyrethroids or ChE inhibitors)
Microbial agents
B thuringiensis and other entomopathogens, targeting lepidopterea, flying insects, nematodes
Granulosis virus – affecting lepidoptera
Details of Chemical Structures by MOA
Compounds with Multi-site Activity IRC 8
Fumigants typify compounds with multi-site activity, with effects on insects, nematodes, and plants, used to sterilize soil prior to planting, and as post-harvest commodity treatments.
Halogentated Fumigants
Many halogenated fumigants had 19th century trials as general anesthetics following the discovery of chloroform and di-ethyl ether, with little or no pre-use safety evaluation. Discarded compounds found multiple other uses., typified by methyl bromide, used as a refrigerant, then as a fire retardant before its general use as a fumigant
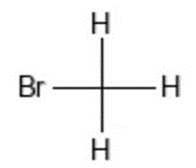
20th century discoveries included ethyline dibromide, initially used as an additive to preventing lead engine build-up in gasoline the containing the anti-knock compound tetraethyl lead.
Neifert described the insecticidal properties of halogenated fumigants in a report for USDA in 1924. Their systematic application as fumigants began in the 1940’s, as indicated by a feature article in a Salinas, Ca newspaper in 1947, describing increased crop yields in experimental studies with ethylene dibromide and D-D mixture (DPR chemcode 185 1,2-dichloropropane, CAS # 78-87-5; PCID), 1,3-dichloropropene and related c3 compounds)


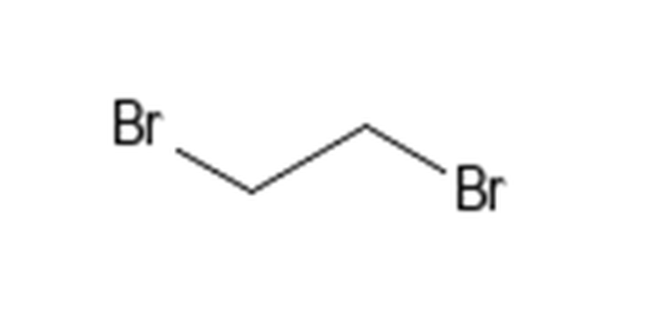
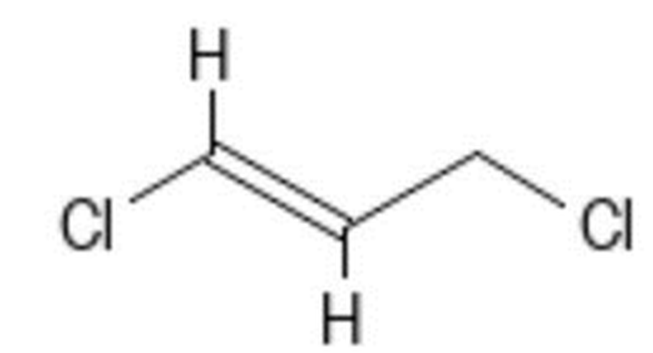
Halide fumigants used in 1974 and not used in 2016 included 1,2 dibromochloropropane (DBCP), ethylene dibromide, ethylene dichloride, and the D-D mixture (chemcode 185 1,2-dichloropropane (CID6564). Most have a high degree of reactivity and present safety issues because of their flammability, irritant properties (excerpts from pubchem warning information shown below), and toxic effects on insects, plants, fungi, nematodes, and vertebrates.
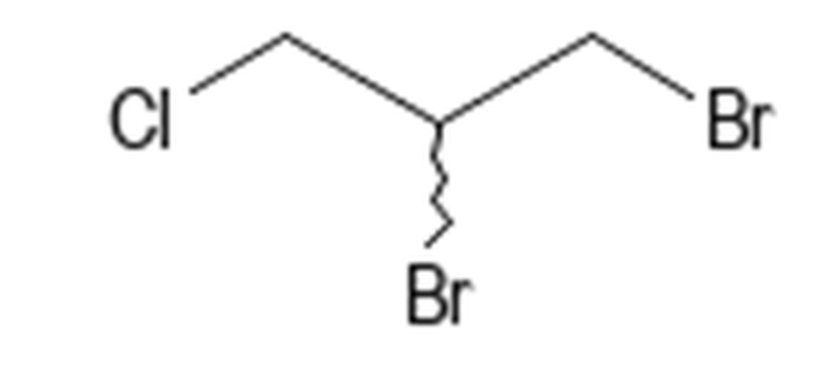
Dibromochloroprone (DBCP) had extensive use because of its limited phytotoxicity and its water solubility, allowing post-plant treatments to control nematodes.
Methylisothiocyanate (MITC Releasers)
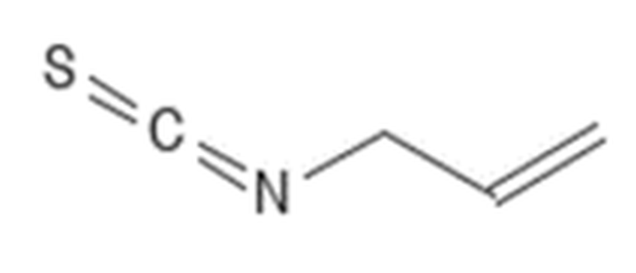
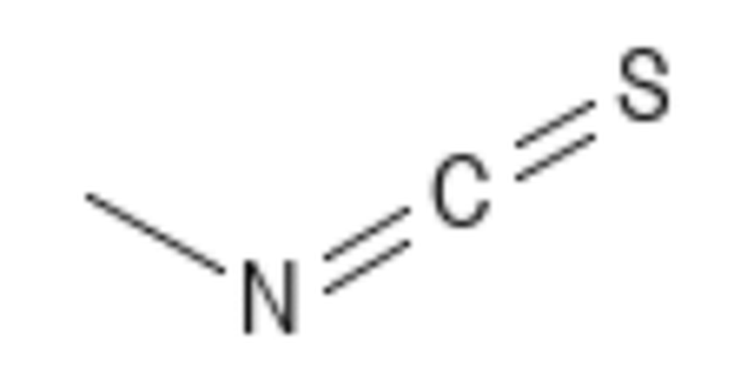
Methyl isothiocyanate – CID 11167 MITC CAS # 556-61-6
Methyl isocyante CID CAS
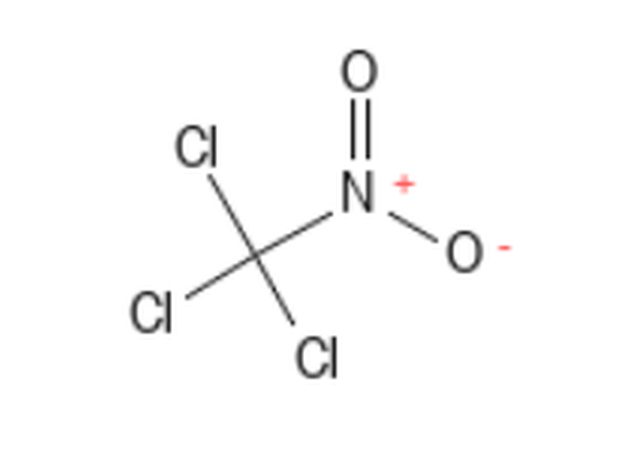
Chloropicrin (Trichloronitromethane) CID: 6423 CAS # 76-06-2; MF: CCl3NO2; MW: 164.37g/mol
Elemental sulfur, oxides, sulfides, acids
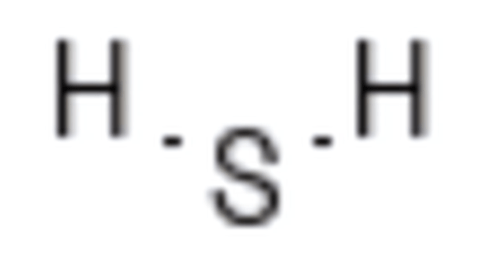
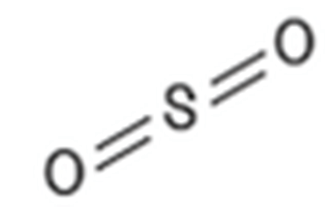
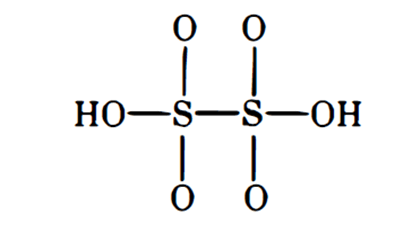
MOAs targeting nervous system
Cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitors
Carbamates – reversible ChE inhibitors – originally identified from the Calabar bean
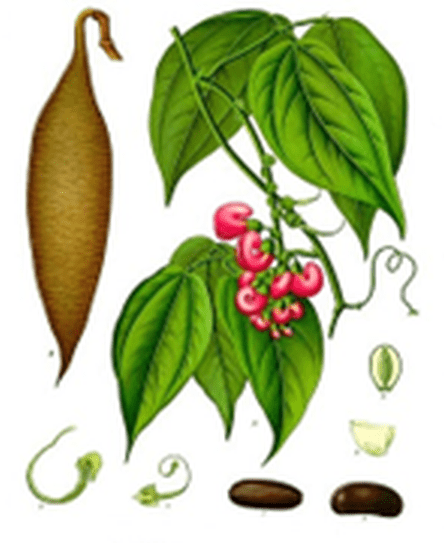
Calabar Bean Physostigma venenosum

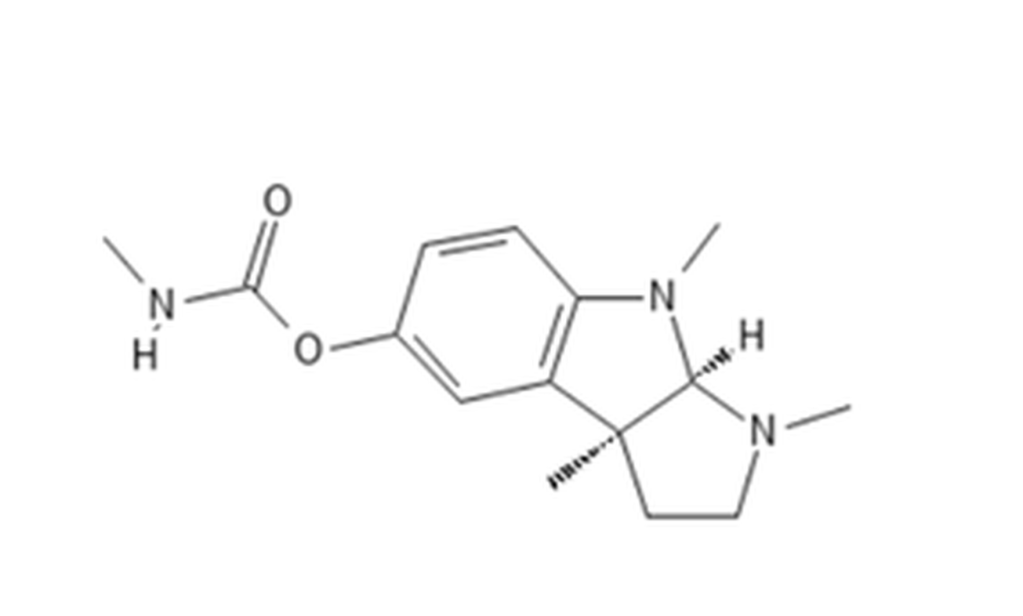
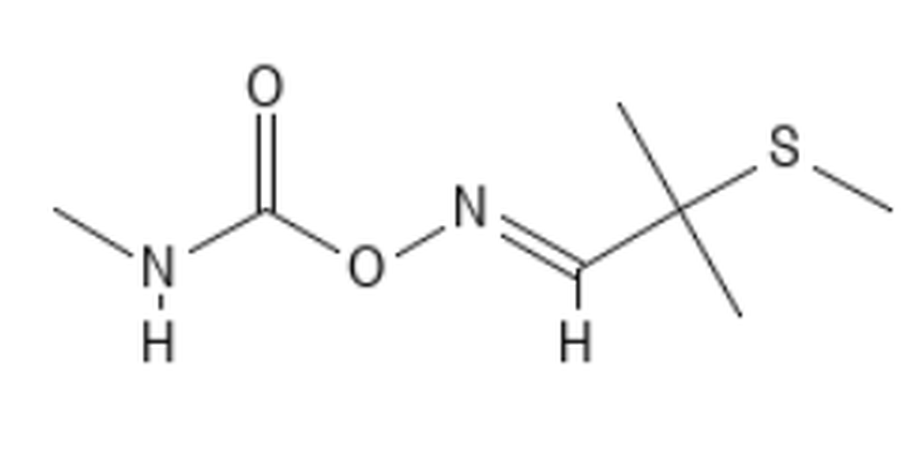
Methomyl CID
Organophosphates
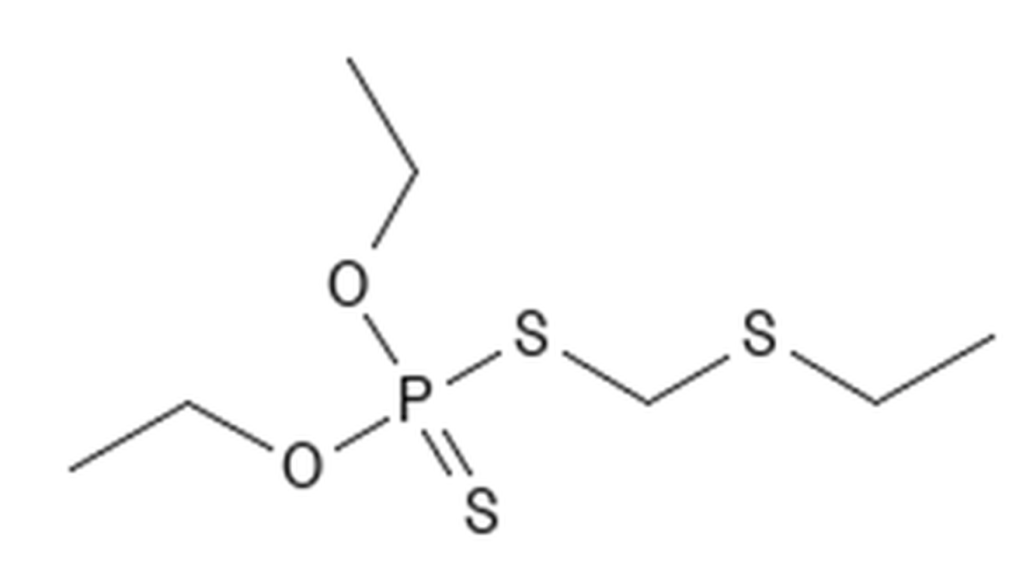
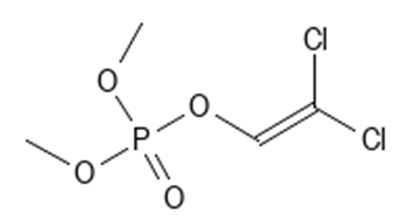
Leave a comment