2.3.1.1 Arsenic compounds
As shown in the history of pesticide use timeline (Word press – https://wordpress.com/post/chemonitoring.tools/166), arsenic insecticides had widespread use after agricultural agents reported success in controlling the Colorado potato beetle outbreak in 1867. In 1950 a published study documented the persistent use of the arsenic insecticides – – Calcium arsenate (38,842 lb) and lead arsenate (27,490 lb), 1974 use data showed use of lead arsenate, sodium arsenate, and sodium arsenite. Available information records indicate use for both agricultural and structural pest control.
2.3.1.1.1 California arsenic groundwater data
A review of samples showing arsenic above the maximum contamination limit (MCL) set by US EPA showed high levels in Delano, an agricultural community 32 miles north of Bakersfield, Ca.
• Highest sampling rate in the state between 2019 and Aug 2022; • 1,516 samples across multiple sample sites: 699 samples (46.1%) were above MCL (10ug/L) ; Highest sample: 32ug/L
Statewide review of samples with detectable levels of either lead or arsenic A review of all wells positive for either lead or arsenic showed indvidiual samples positive for both lead and arsenic, but the publicly available reports did not identify specific compounds in the samples.
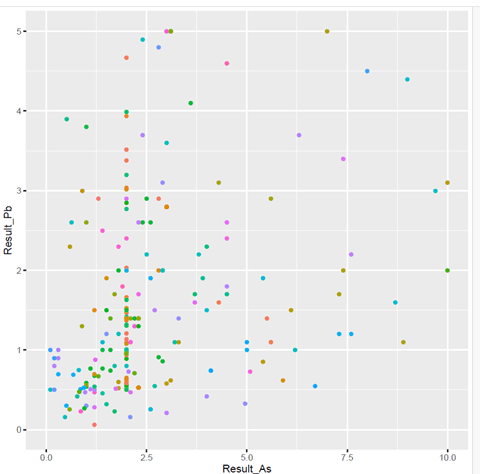
High levels in samples at or adjacent to Edwards Air Force Base (desert area 83 miles south and east of Bakersfield) could have resulted from either agriculture or structural use of arsenic. Military housing on the AFB also had sources of lead in paint and arsenic from household use or geologic deposits (arsenic pyrites, similar to those reported in Bangladesh).
A review a meta-analysis by Saint-Jacques describes (Saint-Jacques et al. Environmental Health 2014, 13:44 (http://www.ehjournal.net/content/13/1/44) documented the risk of bladder associated with arsenic in drinking water.
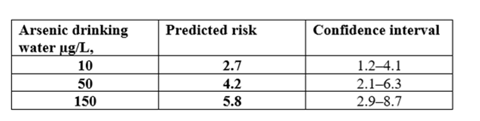
Because of lead’s developmental toxicity any detectable lead presents a hazard to exposed children.
Southeastern US
A forest service review of dipping operations in the southeast US included a detailed history of tick fever outbreaks, quarantines, and changing treatments dating back to the 19th century.
https://www.fs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/stelprdb5396091.pdf Arsenic and Old Bovine Lace – History of the Cattle Tick Eradication Program in the South By Robert G. Pasquill, Jr., Forest Archeologist National Forests in Alabama sSeptember 2012
Sampling conducted in 2006– showed contamination of both soil and water samples
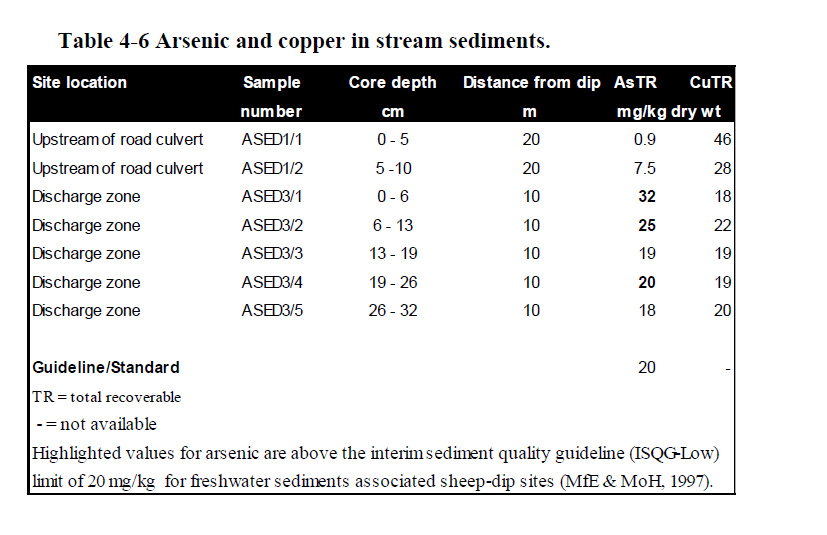
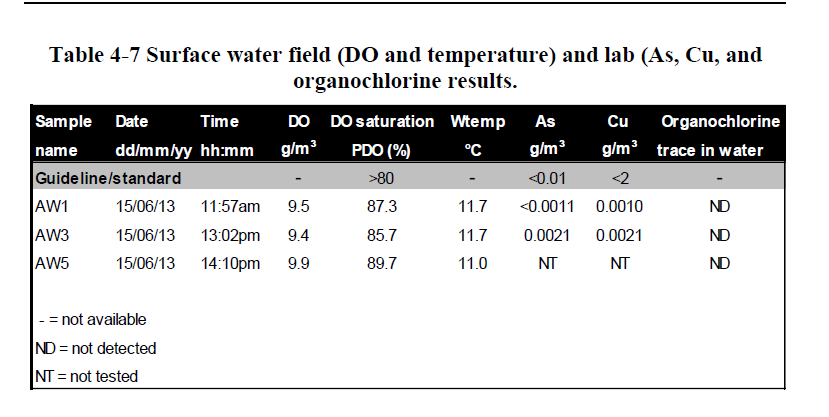
A 2017 University of Waikato PhD thesis – evaluated residues of sheep dip sites

New Zealand dipping operations employed Arsenic/cupper dips between 1840’s and 1961, sodium channel DDT and Gaba Channel dienes (lindane, dieldrin and aldrin) between 1945 and 1961, and pyrethroids or organophosphates since the 1960s.
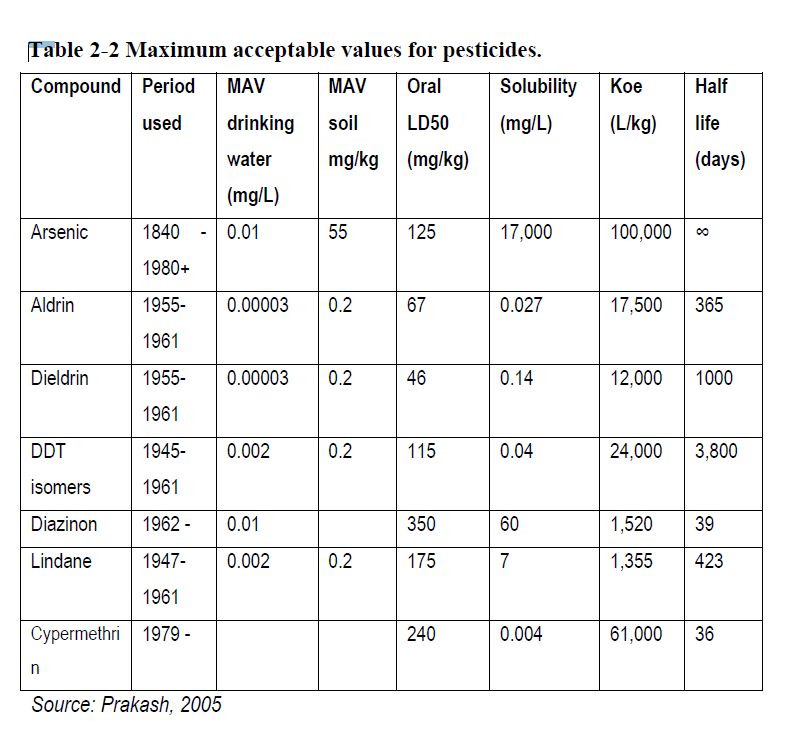
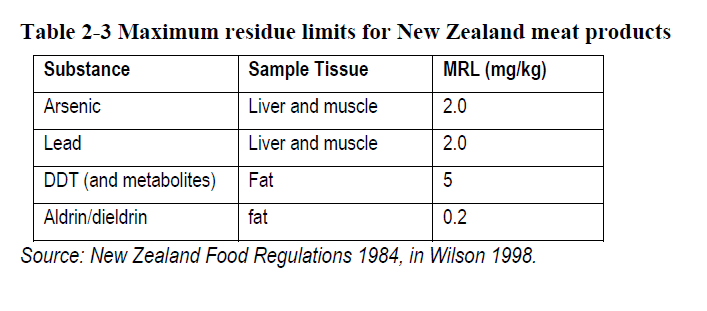


Leave a comment